PASS - Productivity Acceleration Support Services: Empowering Rural Households through Innovation and Formalization
The Productivity Acceleration Support Services (PASS) initiative is a transformative program coordinated by the Countryside Innovations Network (CIN), supported by the Science Technology and Innovation (STI) Secretariat of the Government of Uganda. PASS is designed to accelerate rural socio-economic transformation by empowering households and micro-enterprises through the adoption of Science, Technology, and Innovation (STI).
Mission
Key ComponentsPASS aims to formalize informal enterprises, improve productivity, and foster innovation in rural communities. By transitioning households from informal subsistence activities to accredited enterprises, PASS helps drive wealth creation, market access, and sustainable development.
Key Components
- Mindset Transformation: PASS delivers mindset change programs to encourage entrepreneurial thinking and innovation adoption among rural communities.
- Business Skilling & Incubation: Tailored training and incubation support are provided to rural enterprises to enhance business management, product innovation, and competitiveness.
- Accreditation & Certification: PASS guides informal businesses through the formalization process, offering accreditation and certification services.
- Enterprise Clustering: Rural businesses are aggregated into clusters to enhance market access and improve competitiveness.
- Subscription & Commission-Based Models: Continuous business support is offered through subscription services, while commissions are generated through market linkages
Impact
PASS focuses on enhancing human capital, promoting STI-led practices, and fostering socio-economic growth. It is designed to catalyze regional development by supporting the creation of sustainable enterprises, increasing household income, and driving industrial growth across Uganda.
Integrated model for recovery and utilization of value-added products from agro-wastes
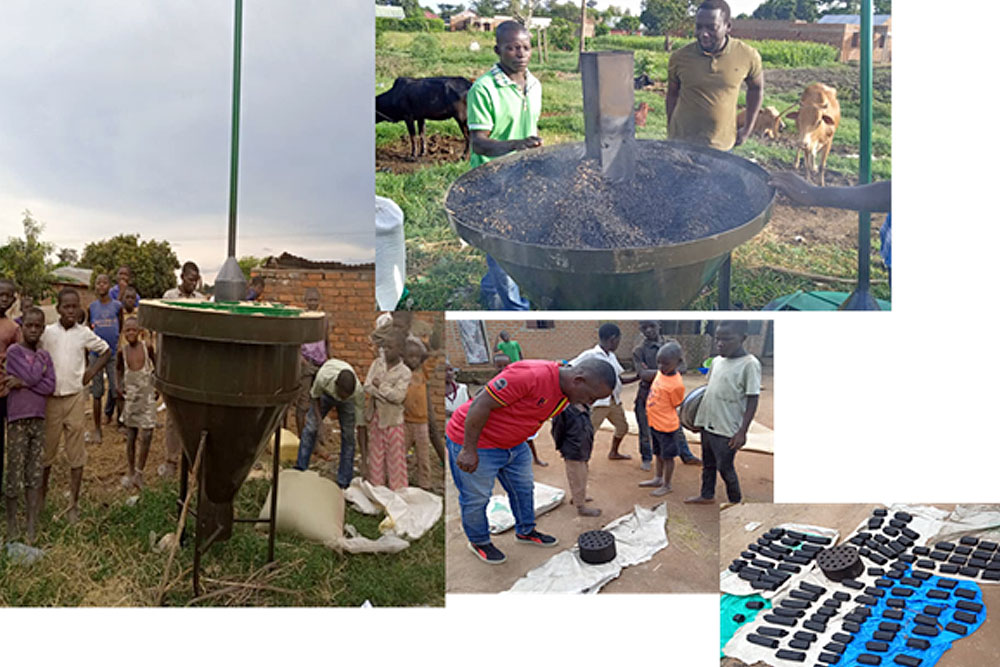

Research on Indigenous poultry production
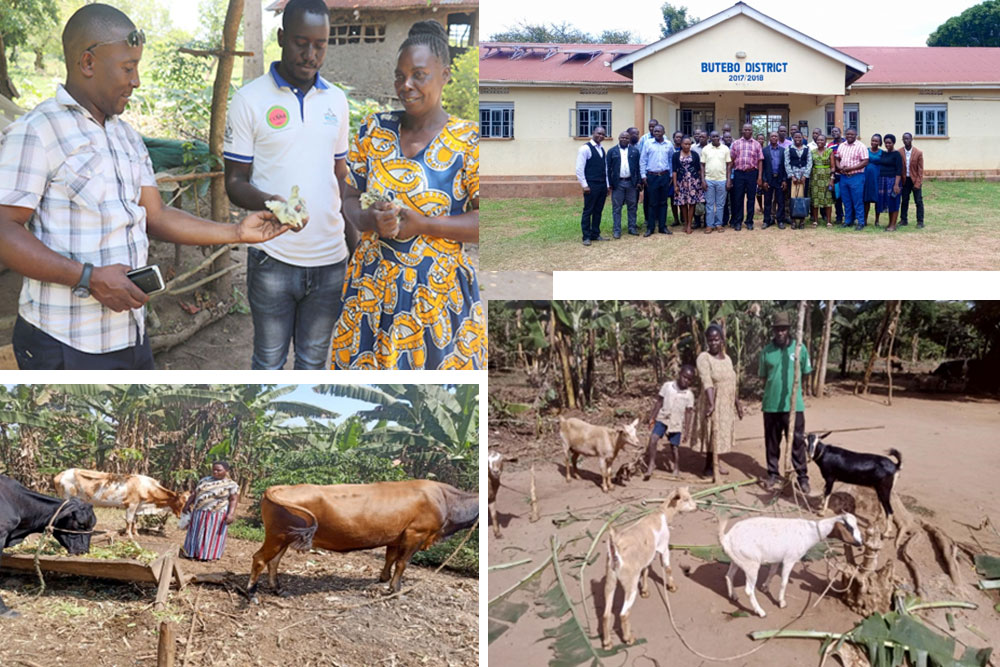

INTRODUCTION TO CIN PASS MODEL
The Productivity Acceleration Support Services (PASS) is a transformative, science-driven initiative under the Countryside Innovations Network (CIN), aimed at accelerating rural socio-economic transformation through the adoption of Science, Technology, and Innovation (STI). PASS helps rural households transition from informal activities into formal, accredited enterprises, driving wealth creation, productivity growth, and sustainability.
PASS is a model that accelerates rural transformation by formalizing the informal economy, enhancing human capital, and promoting sustainable socio-economic growth through STI adoption, creating a model for regional and national impact.
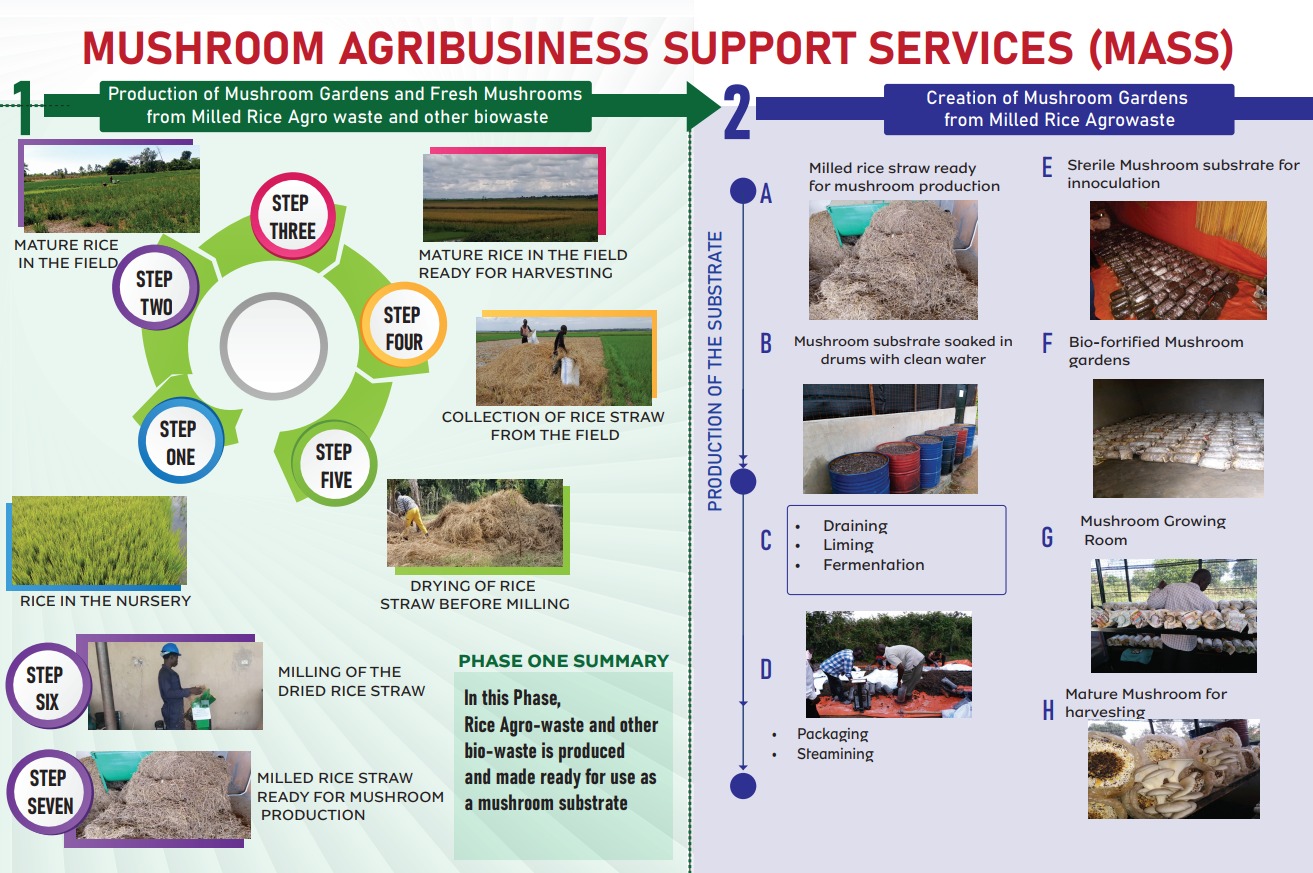
Mushroom Agribusiness Support Services (MASS) Initiative.
About MASS
The Mushroom Agribusiness Support Services (MASS) project, supported by the Government of Uganda through the Science-Technology-Innovation (STI) Secretariat, aims to revolutionize rural livelihoods in the Bukedi sub-region through science-driven cyclic agro-industrial innovations. The venture focuses on sustainable mushroom production by utilizing abundant agricultural by-products such as rice straw and Azora weed as substrates.
Key Objectives:
- Mushroom Production & Value Addition: MASS is scaling up commercial mushroom production to meet high demand for fresh mushrooms and developing value-added products like mushroom-based snacks, powders, and supplements.
- Farmer Empowerment: The project trains rural households in mushroom farming techniques, providing certification and support to enhance income opportunities and improve food security.
- Sustainability Focus: MASS adopts cyclic economy principles by recycling agro-waste, employing vertical farming techniques, and integrating environmental controls to optimize production efficiency and profitability.
- Market Expansion: The project plans to scale operations across eastern Uganda and explore international markets, particularly in East Africa, while securing necessary certifications for cross-border trade.
By aligning with Uganda’s Vision 2040, the venture aims to create jobs, foster agro-industrialization, and contribute to sustainable economic growth in the region.
Preamble to mushroom agribusiness in Bukedi sub-region
Mushroom farming presents a lucrative agribusiness opportunity, driven by rising demand for both fresh and processed mushrooms. With favourable agro-climatic conditions and access to agricultural waste products for substrates, mushroom farming is set to thrive. This analysis highlights key trends, consumer preferences, and market potential, showcasing how mushroom farming can provide sustainable income for local farmers.
Global Mushroom Market Overview
Mushroom Market in AfricaThe global mushroom market is rapidly expanding, valued at USD 50 billion in 2022 and projected to grow to USD 86 billion by 2030 at a 7.9% CAGR. The increasing demand for plant-based and organic food sources is driving this growth, positioning mushrooms as a vital crop in global food security efforts.
Mushroom Market in Africa
In Africa, mushroom farming is gaining traction due to its low land and water requirements. South Africa and Kenya lead the continent in mushroom production, but Uganda is emerging as a key player, especially in urban markets where demand for organic produce is increasing.
Demand Analysis in Uganda
Uganda’s mushroom market is marked by growing consumption, particularly in urban centres such as Kampala. The Uganda National Mushroom Growers Association (UNMGA) projects that demand will grow by 10-12% annually, driven by health-conscious consumers. Currently, Uganda produces 450 tons of mushrooms annually, with demand estimated at 900 tons, presenting a significant supply gap.
- Current Demand: 450 tons produced; 900 tons demanded.
- Price Trends: UGX 10,000 - 15,000 per kg for fresh mushrooms, higher for specialty varieties.

Market Potential in the Bukedi Sub-Region
Bukedi offers an untapped market for mushroom production. Currently, most demand is met by imports from other regions. Urban centres such as Mbale and Tororo have seen a 15% annual increase in demand, particularly from hotels, restaurants, and households.
- Export Potential: With proper quality control and marketing, Bukedi mushrooms can access export markets in neighbouring countries like Kenya.
Supply Chain and Distribution
Mushrooms have a short shelf life, making an efficient supply chain crucial. While Bukedi’s supply chain faces challenges like inadequate storage, opportunities exist for local and regional sales, with strong export potential.
Competitive Landscape
Bukedi faces minimal competition, as mushroom farming is still underdeveloped in the region. The main competition comes from central and western Uganda. Bukedi’s advantages include proximity to raw materials (rice straw) and favourable year-round growing conditions.
Profitability of Mushroom Farming
Mushroom farming in Bukedi is highly profitable, with low production costs and high market prices. A 10m² mushroom garden can yield 200-300 kg per cycle, generating revenues of UGX 2,000,000 - 4,500,000 per year.
Consumer Preferences
Health-conscious consumers are driving mushroom demand. Mushrooms are recognized as a superfood, rich in protein, vitamins, and antioxidants. Specialty mushrooms like shiitake and oyster are gaining popularity among restaurants and hotels.
Challenges
Despite the potential, mushroom farming in Bukedi faces some challenges:
- Access to Quality Spawn: Limited availability of high-quality mushroom spawn.
- Farmer Training: Lack of awareness and training in modern farming techniques.
- Post-Harvest Losses: Mushrooms are highly perishable, requiring adequate storage facilities.
Recommendations
To fully tap into the mushroom market, the following recommendations are critical:
- Capacity Building: Training programs on farming techniques and post-harvest management.
- Spawn Production: Local spawn production to reduce dependence on imports.
- Storage and Distribution: Investments in cold storage to minimize losses.
- 4. Marketing Campaigns: Promote mushrooms as a nutritious and versatile food.
- 5. Value-Added Products: Explore drying, powdering, and canning to extend shelf life and increase market reach.
Conclusion
Mushroom farming offers a promising and profitable agribusiness opportunity in Bukedi. With growing local and regional demand and the potential for export, mushroom cultivation can contribute to the economic growth of the region. By addressing production and marketing challenges, Bukedi can establish itself as a key player in Uganda’s mushroom market.